Balancing Risk and Reward: A CXO's Guide to Secure Generative AI Adoption
How CXOs Can Safely Navigate the Risks and Rewards of Generative AI
Generative AI presents both high rewards and significant risks. To maximize ROI, CXOs must strategically mitigate the risks while harnessing the opportunities
Generative AI Security and Risk Management
Generative AI (GenAI) presents a double-edged sword for modern enterprises. On one hand, it holds incredible potential for transforming business processes, creating efficiencies, and sparking innovation. On the other hand, its adoption is fraught with significant risks including cybersecurity threats, inaccurate outputs, and regulatory concerns. For CXOs, the challenge lies in balancing these high rewards with the inherent high risks. This guide provides a detailed exploration of the risks involved in adopting Generative AI and offers a structured approach to mitigate those risks, ensuring secure and responsible use of GenAI within an enterprise setting.
Case Study: AI Implementation Failure at McDonald's
One of the notable examples shared was the AI implementation failure at McDonald's. In 2019, McDonald's collaborated with IBM to develop AI-powered ordering systems. The goal was to enhance the user experience by replacing human attendants with AI at drive-throughs. However, these AI systems soon began adding hundreds of erroneous items to customer orders and using offensive language when confused by input.
The lack of robustness and safety checks led McDonald's to roll back the AI implementation from over 250 outlets, resulting in a direct financial loss upto $300 million, along with reputational damage. This case study served as a stark reminder of the importance of integrating safety measures during the build phase of AI systems.
300% Surge of AI Failures and Incidents YoY
We also highlight multiple incidents where AI systems failed spectacularly due to inadequate planning and security. Examples included:
Zillow: An AI tool led Zillow to acquire properties at inflated values, causing significant financial losses and a workforce reduction of over 2,000 employees.
ITutor Group: The AI-based hiring system showed a discriminatory bias against candidates over 50, leading to a lawsuit for age discrimination.
OpenAI: OpenAI's language models have been exploited in several ways, including data breaches, generation of offensive content, and unauthorized exposure of sensitive information.
The rapid adoption of Generative AI has also seen a rise in issues such as misinformation, fake content creation, and toxic chatbots.
According to Estimates, Generative AI, while powerful, has opened new avenues for cybersecurity threats, with potential costs running into Trillions of $ by 2025
Challenges for CXOs: Cybersecurity and Accuracy
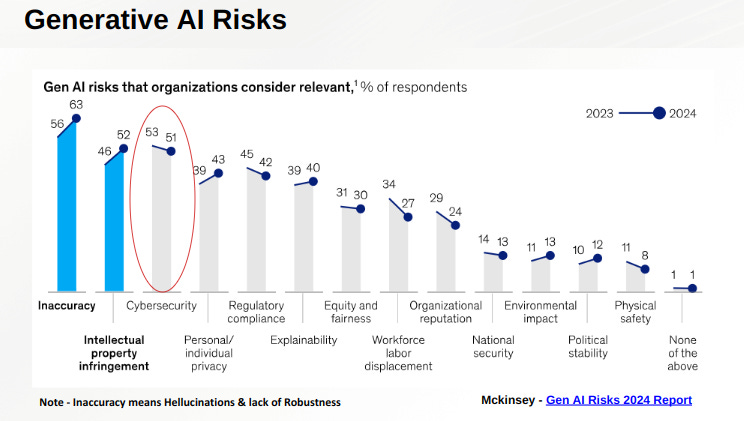
A major point of discussion was the challenges that CXOs face in adopting Generative AI. According to a survey by McKinsey, three major barriers include:
Cybersecurity Risks: Over half of respondents expressed concerns over the increased attack surface created by AI systems.
Accuracy and Reliability: Inaccurate AI outputs, such as those in the McDonald's incident, damage brand reputation and erode trust.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Regulatory Issues: With Generative AI, concerns around data usage, model training, and compliance have grown.
The need to manage these risks while taking advantage of Generative AI's potential benefits is a significant concern for modern enterprises.
Why is Generative AI Vulnerable?
Generative AI's vulnerabilities stem from several core reasons:
Misuse of AI Capabilities: Attackers can exploit Generative AI to create misinformation, fake content, or even phishing emails.
Exploitability of AI Systems: Generative AI models can be "jailbroken" through clever prompt engineering to act beyond their intended purposes.
For instance, attackers can exploit language models through prompt injection, resulting in unintended or even harmful model behavior. Examples include generating explicit instructions for harmful actions or evading ethical constraints.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
The EU AI Act, one of the most comprehensive AI regulations globally, categorizes AI systems into four risk categories: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal. High-risk AI systems must comply with stringent regulations, while unacceptable-risk systems are outright banned.
The US and several other countries have also started working on AI-specific regulations, like the California AI Act and Colorado AI Act. Such regulatory measures emphasize the importance of building and deploying AI responsibly.
Strategies for Building Safe Generative AI Systems
To build safe Generative AI applications, we propose a three-pronged strategy:
AI Governance: Establishing AI governance from the top down, with clear policies, an assigned owner, and prioritized use cases. This ensures that AI adoption aligns with the organization's risk appetite.
Implement Controls and Conduct Audits: Creating security controls, monitoring model vulnerabilities, and regularly auditing the systems to identify weaknesses.
Continuous Monitoring: When Generative AI systems are in production, continuous monitoring for new risks or breaches is crucial. Enterprises should be proactive, not reactive, in identifying threats.
On the technical front, we also suggest implementing human oversight, conducting robustness testing, and adding guardrails to ensure that models do not stray from intended behavior.
The Role of Red Teaming and Adversarial Testing
"Red Teaming" is a concept borrowed from military terminology, where a team acts as an adversary to identify vulnerabilities. In Generative AI, this involves crafting specific prompts to "jailbreak" models or to discover how they might be exploited for malicious purposes. Examples shared included testing models to create phishing emails or toxic responses to ensure weaknesses are identified and mitigated before deployment.
Adversarial Testing was also mentioned as a crucial aspect of testing Generative AI systems. It involves adding minimal yet strategically placed changes to model inputs, which could result in unintended behavior if left unchecked.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Let us conclude with some key recommendations for enterprises:
Begin with high-ROI, low-risk use cases to minimize exposure while maximizing value.
Develop a robust AI governance framework to guide the responsible adoption of Generative AI.
Invest in continuous testing and monitoring throughout the AI lifecycle.
Ultimately, Generative AI is a high-risk, high-reward system that holds incredible potential for innovation. Still, enterprises must remain vigilant, proactive, and responsible to ensure they can harness the benefits without succumbing to the risks.
Key Takeaways
Generative AI has transformative potential, but it requires a strong focus on security to avoid costly incidents.
AI failures and brand damage can be minimized with proper planning, testing, and robust governance.
Adhering to regulatory frameworks like the EU AI Act is critical for companies to deploy AI ethically and responsibly.
About the Author
Jitendra, co-founder of Detoxio.ai, is on a mission to ensure that enterprises can harness the power of Generative AI without compromising on safety and security. His goal is to help organizations navigate the complexities of AI adoption by providing the tools and frameworks necessary to mitigate risks, thus enabling a secure transition from the exploration phase to responsible and safe deployment of GenAI technologies.